Problem #2: pH and EC Imbalances in Hydroponics – Challenges and Solutions
In hydroponic farming, maintaining the right pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC) levels is crucial for plant health and productivity. Unlike soil-based systems, where the soil acts as a natural buffer, hydroponics relies entirely on the grower to manage these parameters. Even small imbalances can lead to nutrient deficiencies, toxicities, or stunted growth.
In this post, we’ll explore why pH and EC imbalances occur, their impact on hydroponic crops, and practical solutions to keep these levels in check.
Why Are pH and EC Imbalances So Critical in Hydroponics?
pH and EC are two of the most important factors in hydroponic systems because they directly affect nutrient availability and plant uptake. Here’s why they matter:
pH Imbalances:
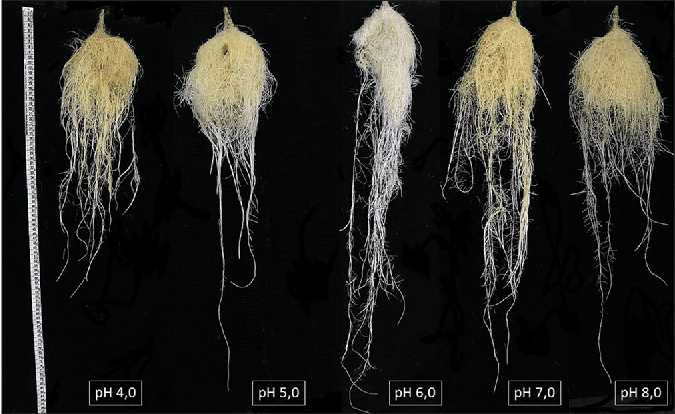
pH measures how acidic or alkaline the nutrient solution is. Most hydroponic plants thrive in a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5.
If the pH is too high (alkaline), nutrients like iron, manganese, and phosphorus become less available.
If the pH is too low (acidic), nutrients like calcium and magnesium may become inaccessible.
EC Imbalances:
EC measures the concentration of dissolved salts (nutrients) in the water. It indicates whether the nutrient solution is too strong or too weak.
High EC levels can cause nutrient burn, while low EC levels can lead to deficiencies.
Dynamic Nature of Hydroponics:
pH and EC levels fluctuate over time due to nutrient uptake, evaporation, and microbial activity. This makes constant monitoring essential.
Consequences of pH and EC Imbalances
Ignoring pH and EC levels can have serious consequences for your hydroponic crops:
Nutrient Lockout:
Improper pH levels can lock out essential nutrients, even if they’re present in the solution. This leads to deficiencies and poor plant growth.
Nutrient Toxicity:
High EC levels can cause nutrient burn, characterized by brown or crispy leaf edges and stunted growth.
Reduced Yields:
Imbalances stress plants, reducing their ability to photosynthesize and produce fruits or flowers.
Increased Susceptibility to Disease:
Stressed plants are more vulnerable to pests and pathogens, which can spread quickly in a hydroponic system.
Wasted Resources:
Incorrect pH or EC levels can render your nutrient solution ineffective, leading to wasted water, fertilizers, and energy.
Solutions for Managing pH and EC Imbalances
To maintain optimal pH and EC levels, hydroponic growers must adopt a proactive and systematic approach. Here are some proven strategies:
1. Monitor pH and EC Daily
Use a pH meter and EC meter to check levels daily. Calibrate your meters regularly to ensure accurate readings.
2. Adjust pH as Needed
If the pH is too high, use a pH down solution (usually containing phosphoric acid) to lower it.
If the pH is too low, use a pH up solution (usually containing potassium hydroxide) to raise it.
Make gradual adjustments and retest after each change.
3. Maintain Optimal EC Levels
Follow the recommended EC range for your specific crop. For example:
Leafy greens: 1.2–2.0 mS/cm
Fruiting plants: 2.0–3.5 mS/cm
If EC is too high, dilute the nutrient solution with fresh water.
If EC is too low, add more nutrients to the solution.
4. Use High-Quality Water
Start with clean, filtered water to avoid introducing contaminants or imbalanced minerals. Reverse osmosis (RO) water is ideal for hydroponics.
5. Follow a Feeding Schedule
Different growth stages require different nutrient concentrations. Use a feeding chart provided by your nutrient manufacturer to adjust the solution as your plants grow.
6. Flush the System Regularly
Over time, salts can build up in the system, affecting pH and EC levels. Flush the system with clean water every 2–3 weeks to prevent this.
7. Use Buffering Agents
Some nutrient solutions contain buffering agents that help stabilize pH levels. Look for products labeled as “pH-stable” or “buffered.”
8. Automate Monitoring and Adjustments
Invest in automated pH and EC controllers that monitor levels in real-time and make adjustments as needed. This is especially useful for large-scale operations.
Advanced Tips for Managing pH and EC
For experienced growers looking to optimize their systems further, consider these advanced techniques:
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT):
This system continuously circulates a thin film of nutrient solution, ensuring consistent pH and EC levels.
Drip Irrigation Systems:
Drip systems allow precise control over nutrient delivery, reducing the risk of imbalances.
Leaf Tissue Analysis:
Periodically test leaf tissue to identify nutrient deficiencies or toxicities that may not be visible yet.
Microbial Inoculants:
Beneficial microbes can help stabilize pH and improve nutrient uptake. Look for products containing mycorrhizae or beneficial bacteria.
Conclusion
pH and EC imbalances are among the most common challenges hydroponic growers face, but they’re also among the most manageable. By understanding the importance of these parameters, monitoring them regularly, and adopting best practices, you can ensure your plants receive the nutrients they need to thrive.
Investing in quality equipment, following a feeding schedule, and automating adjustments can save you time and resources while maximizing yields. With proper management, pH and EC imbalances won’t stand in the way of your hydroponic success.




